SleepViT: a compact vision transformer accelerator for sleep stage classification in wearable devices
- Volume
- CitationRobitaille T, Liu X. SleepViT: a compact vision transformer accelerator for sleep stage classification in wearable devices. Neuroelectronics 2026(1):0002, https://doi.org/10.55092/neuroelectronics20260002.
- DOI10.55092/neuroelectronics20260002
- CopyrightCopyright2026 by the authors. Published by ELSP.
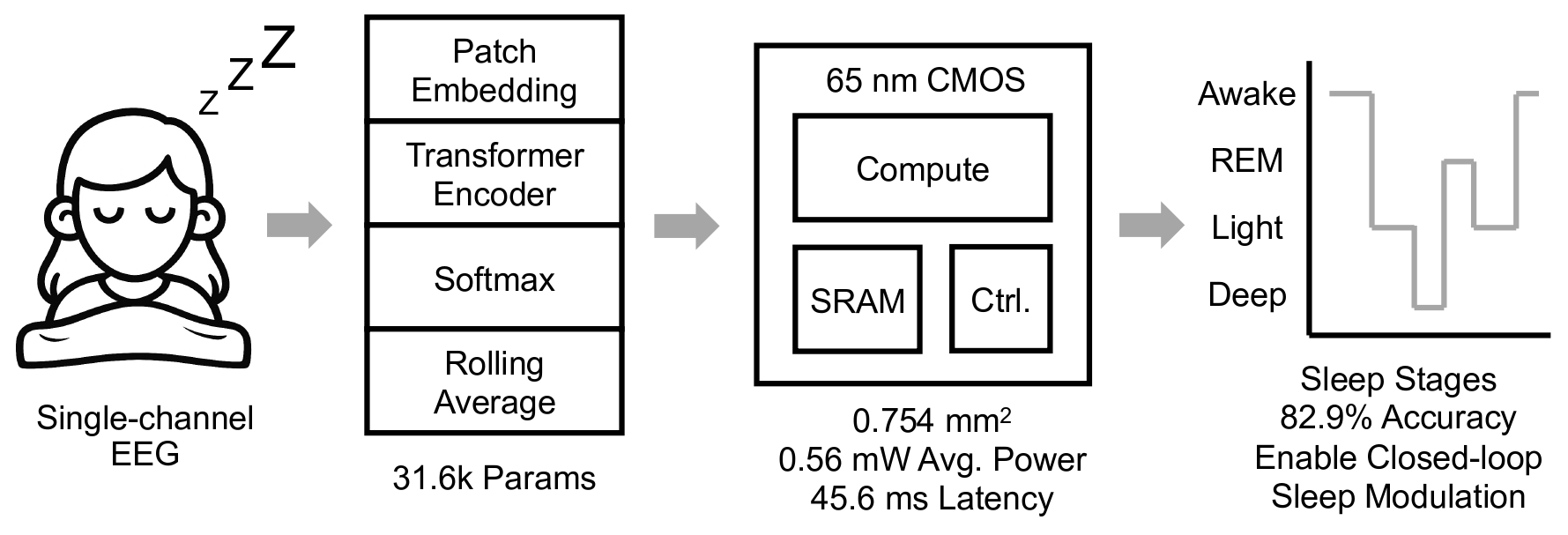
This paper presents SleepViT, a custom accelerator for real-time, low-power sleep stage classification in wearable devices. At the core of SleepViT is a lightweight vision transformer model specifically optimized for electroencephalogram (EEG)-based sleep stage classification. The model is trained on the MASS SS3 dataset and achieves a classification accuracy of 82.9% across four sleep stages, while requiring only 31.6 k parameters, demonstrating its suitability for embedded inference. The proposed transformer is designed, synthesized, and fully placed and routed in 65 nm CMOS technology. To minimize power and area, the architecture adopts a layer-dependent fixed-point quantization scheme, variable data widths, and optimized memory access patterns. The placed and routed accelerator occupies 0.754 mm2 of silicon, operates at a maximum clock frequency of 379 MHz, and consumes 6.54 mW dynamic and 11.0 mW leakage power with an average inference time of 45.6 ms. With power gating during idle periods, the effective average power is 0.56 mW, enabling extended battery life in wearable devices. This work demonstrates the feasibility of deploying transformer-based models in highly constrained edge environments and provides a pathway for future biomedical application specific integrated circuits (ASICs) that require both real-time performance and ultra-low power consumption.
vision transformer; ASIC; edge AI; sleep stage classification; wearable device

 X
X Facebook
Facebook LinkedIn
LinkedIn Reddit
Reddit Bluesky
Bluesky