Volumes & Issues
Contact
For any inquiries regarding journal development, the peer review process, copyright matters, or other general questions, please contact the editorial office, Ms. Malina Luo, E-Mail: smartcon@elspub.com.
For production or technical issues, please contact the production team, Mr. Jay Zhuang, E-Mail: production@elspub.com.
No items found.
Smart Construction: digitization and intelligence transformation
DOI: 10.55092/sc20240006
Received: 15 Dec, 2023
Accepted: 23 Dec, 2023
Published: 24 May, 2024
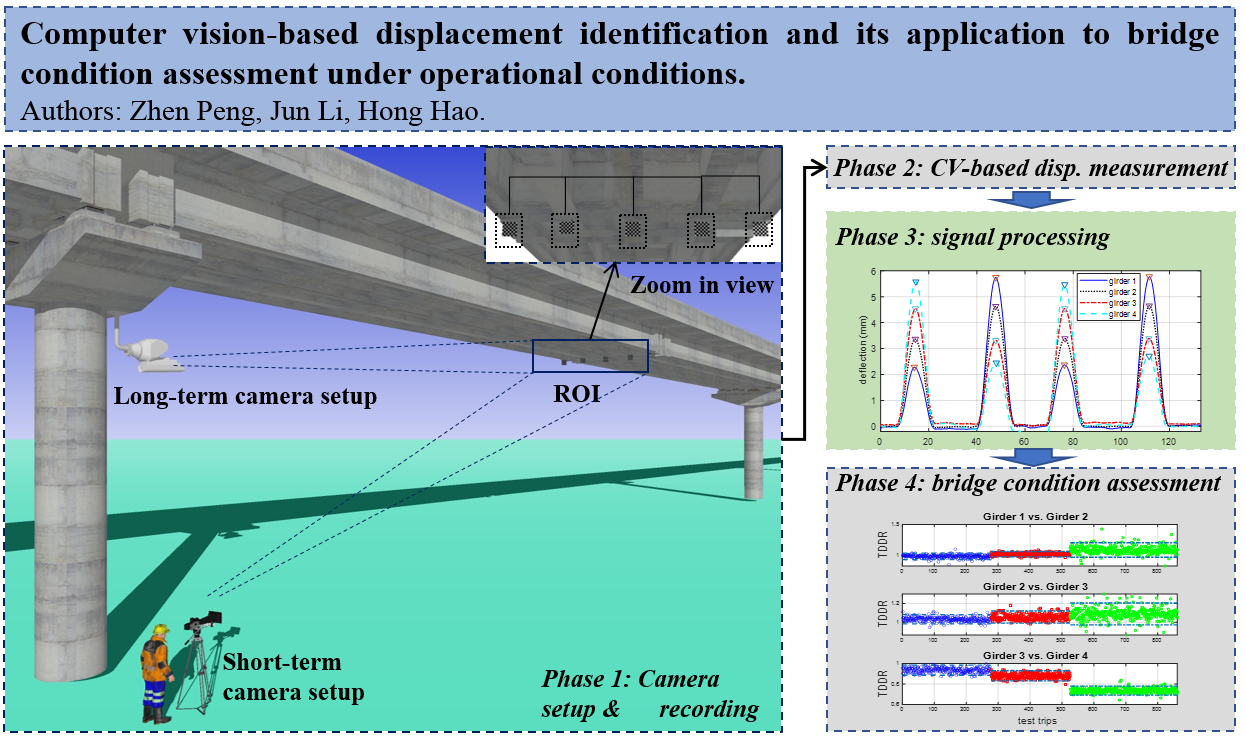
Computer vision-based displacement identification and its application to bridge condition assessment under operational conditions
DOI: 10.55092/sc20240003
Received: 27 Jan, 2024
Accepted: 23 Apr, 2024
Published: 26 Apr, 2024
Bridge damage detection is crucial for ensuring the safety and integrity of the bridge structure. Traditional methods for damage detection often rely on manual inspections or sensor-based measurements, which can be time-consuming and costly. In recent years, computer vision techniques have shown promise in bridge displacement measurement and damage detection. The objective of this study is to extract reliable features from displacement measured with computer vision-based method that are sensitive to structural condition change while robust to the variation of operational condition. In particular, thisresearch paper presents a novel approach for bridge damage detection using an indicator defined based on the transverse influence ratio (DTIR) from computer vision-based displacement measurements. The proposed method utilizes computer vision algorithms to extract bridge girder displacement responses under moving load. The DTIR indicator, defined as the vehicle-induced bridge quasi-static displacement ratio between two adjacent girders, is extracted as the damage-sensitive feature. Theoretical derivation proves that DTIR indicator is only related to the structural condition and the transverse position of a vehicle over the deck, while independent of the variation of vehicle weight and speed. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, a series of drive-by experiments were performed on a multi-girder beam bridge with different structural conditions. The results demonstrated the capability of the proposed approach in accurately detecting the occurrence and possible location of structural damage. Furthermore, the paper discusses the advantages and limitations of the DTIR indicator for bridge damage detection, as well as how to generalize the proposed method to bridges with more than two traffic lanes. In conclusion, the proposed method offers a promising solution for low cost, easy deployable and scalable health monitoring solution for bridges under operating conditions.
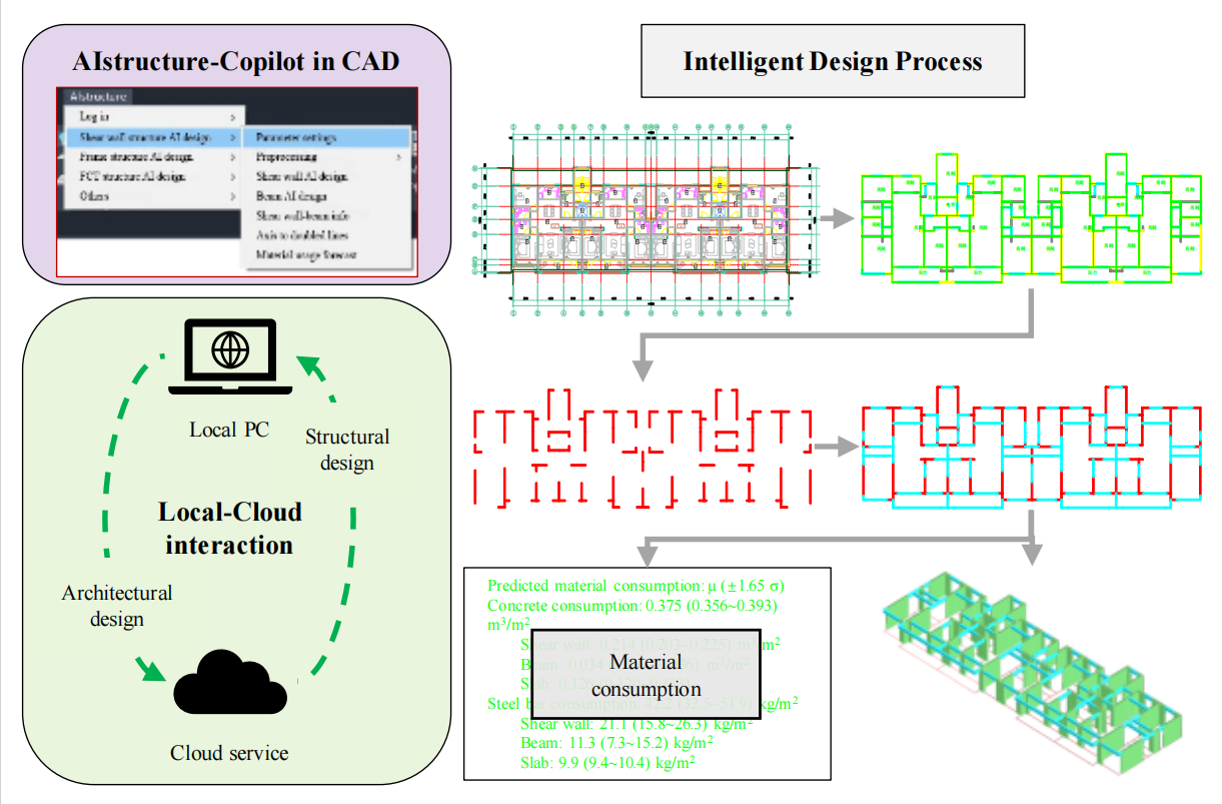
AIstructure-Copilot: assistant for generative AI-driven intelligent design of building structures
DOI: 10.55092/sc20240001
Received: 11 Jan, 2024
Accepted: 28 Feb, 2024
Published: 04 Mar, 2024
The rapid advancement of intelligent design technology in building structures has been primarily implemented in engineering practice through the use of local or cloud-based software to offer intelligent design services. However, local intelligent design services are time-consuming and require high-end hardware, whereas cloud-based designs fail to integrate seamlessly with existing design processes. Consequently, providing convenient intelligent design support for engineering practices is challenging. To address these problems, this study proposes a local–cloud collaborative intelligent design technology called AIstructure-Copilot, which serves as a structural intelligent design assistant. In this system, the local end performs routine graphical operations that align with engineers' design habits, whereas the cloud end executes generative artificial intelligence (AI) for intelligent design, thereby enhancing efficiency and effectively combining the strengths of both services. Specifically, this technology achieves a high level of automation and intelligence throughout the entire process, encompassing architectural design, structural design, and the establishment and execution of structural analysis models. This is accomplished by constructing a local–cloud collaborative mode, introducing a comprehensive data transmission format, and developing a cloud interface for generative AI algorithms. The effectiveness of the AIstructure-Copilot model was validated using a typical case study. The results demonstrate that AI design improves design efficiency by more than tenfold, satisfies the regulatory requirements of design schemes, and exhibits a discrepancy of approximately 20% when compared with designs created by competent engineers.
No items found.
No items found.
No items found.