Engineering lipid nanoparticles with improved endosomal escape for cytoplasmic delivery of RNA drugs
- Volume
- CitationYan Z, Qing G, Liang X. Engineering lipid nanoparticles with improved endosomal escape for cytoplasmic delivery of RNA drugs. Biofunct. Mater. 2025(4):0017, https://doi.org/10.55092/bm20250017.
- DOI10.55092/bm20250017
- CopyrightCopyright2025 by the authors. Published by ELSP.
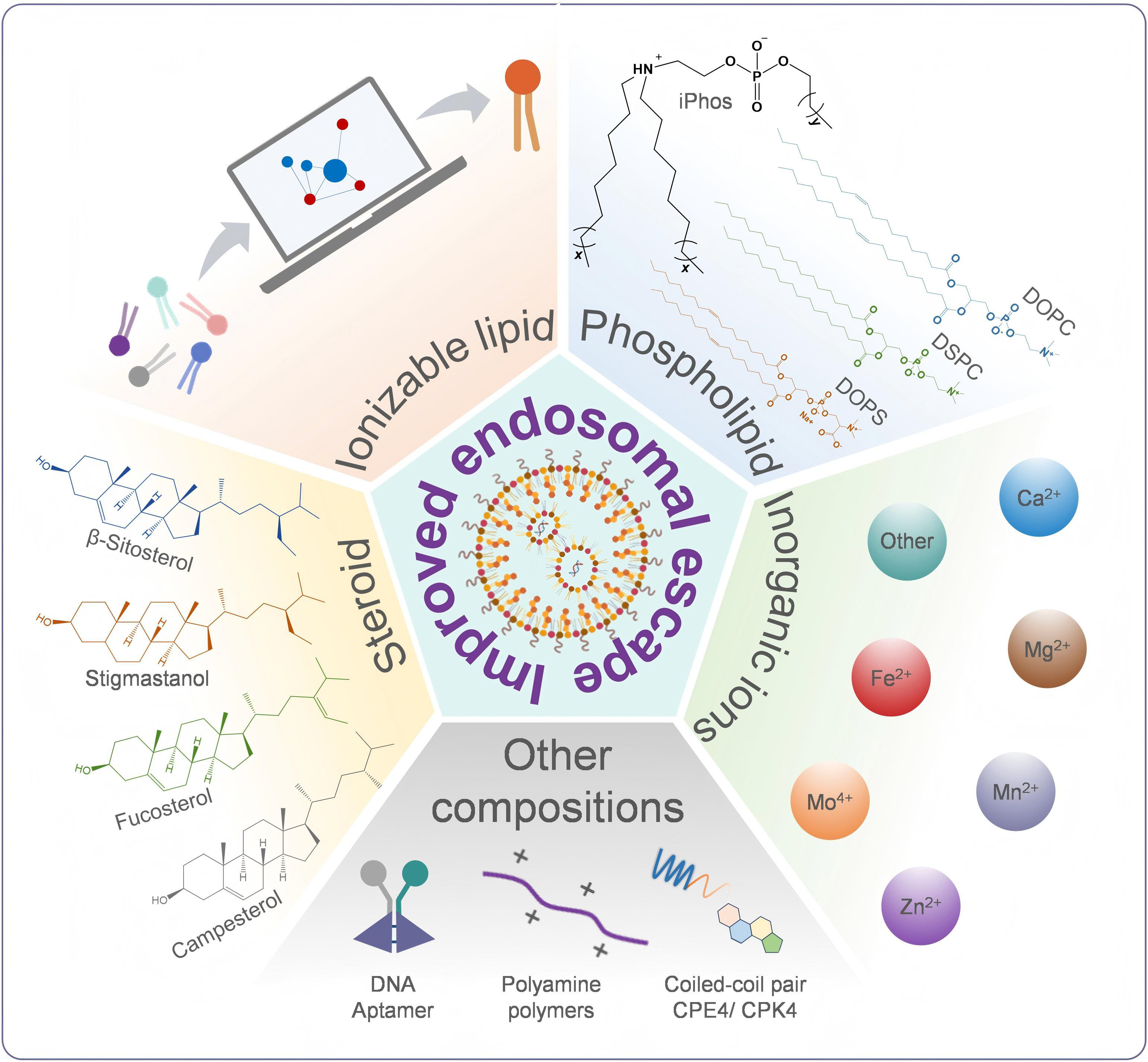
RNA therapy, with its capabilities in regulating physiological processes directly by affecting the central dogma, holds great potential in the prevention and treatment of various diseases. However, RNA-derived drugs typically require proper delivery vectors to function effectively and also face problems such as low delivery rate due to multiple biological barriers, especially in the intracellular endosome-lysosome pathway, where only a small fraction of RNA molecules can escape and enter the cytosol. A variety of RNA delivery vectors have been developed to address those challenges. Among them, lipid nanoparticles are one of the most promising candidates. Proper engineering of the constituents of LNP is a promising approach to facilitate endosomal escape of RNA. In this review, we will discuss the advantages of LNPs, along with the relationship between their molecular constituents and functions. Then, we will introduce several proposed mechanisms of endosomal escape and the properties of LNPs that may influence these mechanisms. Finally, the current efforts in promoting endosomal escape based on lipid molecule modification or the addition of other materials will be presented. Through the comprehensive review of the current status of efficient LNP-based endosomal escape, we hope this review will provide a valuable guideline for the development of promising RNA delivery vectors.
RNA delivery; lipid nanoparticles; endosomal escape; biological barriers

 X
X Facebook
Facebook LinkedIn
LinkedIn Reddit
Reddit Bluesky
Bluesky